- TI nspire
[function] part() // nspire 레퍼런스 가이드북에 없는 함수
1. part()
"Error: Argument must be a Boolean expression or integer"
1.1 part(data) ⇒ (number) index
- data 에서 (계산 우선순위상) 처음 실행되는 function(기능) 이 포함하고 있는 요소(argument) 의 갯수를 반환함.
- data==list,
list 의 element 갯수 - data==matrix,
matrix 열(row) 갯수 - data==expression,
수식에 포함된 기능(연산자(+ - × ÷ ^...) / 함수(cos()...) / "and" / "or" 등등) 중에서, 뭐가 됐든 우선순위가 제일 높은 것에 필요한 요소(argument)의 갯수를 반환함.
1.2 part(data, index)
- index==0 일 때,
data에 포함된 기능을 string 형식으로 반환합니다.
예) "{", "or", "+", "/" - data==list,
list 의 index에 해당하는 요소를 반환 - data==matrix,
matrix index에 해당하는 열(row) 를 list 형식으로 반환 - data==expression,
기능에 사용되는 요소를 순서대로 반환
2. 사용 예시

ㄴ 리스트나, 매트릭스는 이해하기 쉽습니다.

ㄴ 실수나 순허수의 연산자가 없고 자기 자신이 "실수" "순허수"로 기능에 해당합니다. 따라서 요소arguments=0 이 되는 거구요.
ㄴ 순허수가 아닌 복소수는 실수+순허수와 같이 표현되므로 연산자 "+"가 기능에 해당하고, 실수와 순허수가 요소에 해당하여 arguments=2 가 됩니다.
ㄴ 유리수는... 조금 특별한데, 1/2 은 기능이 "1/2"로서 argument=0 이고, √2/2 는 기능이 "/" 이고 arguments=2 입니다.
ㄴ 수식에 연산자가 있더라도 계산에 의해 즉시 단순화되는 경우(1+2+3 = 6) 단순화된 결과를 기준으로 part() 가 실행됩니다.

ㄴ and 와 or 가 나열되어 있는 경우, or 연산자가 우선순위를 갖습니다.
ㄴ or 연산자가 여러개 있을 경우 왼쪽부터 실행됩니다. (and도 동일)
ㄴ or 연산자는 or 를 기준으로 왼쪽과 오른쪽 두개의 요소로 기능이 구현 됩니다. arguments=2 (and도 동일)

댓글7
- 1
- 2
-
3
FireCraft
part처럼 연산자나 함수를 뽑아주는 명령어가 그 cas에 없다면 그게 cas라고 부를 수 있나? 생각됩니다.
전 split( )함수를 구현하면서 (저도 split이란 이름을 붙였습니다) 코드를
split(v1)=func
if part(v1,0)="or"
return augment({part(v1,1)}, {split(part(v2,2))})
return {v1}
end func
이런 방식으로 짰습니다. (이해하기 쉽게 흐름만 보인 것으로 실제 코드는 아닙니다)
솔직히 아랫글 보고 좀 놀란게 part명령어를 일부러 숨겨놓은 것 같은데 part명령어가 없이 기능들을 짤 수 있을까? 생각해 보았습니다 그러면 식을 string으로 잡아서 거기서 찾아내는 방법을 써야되겠다. 와, 근대 그렇게 짜라고? 이런 생각을 했었는데 제가 생각한 방식 그대로 코드가 되어 있어서였습니다 -
세상의모든계산기
[TI-89, 92 plus guidebook] p.477 에 멀쩡하게 나와 있네요.
제가 nspire part() 로만 검색해서 도통 안나왔었나봅니다.
part() CATALOG
part(expression1[,nonNegativeInteger])
This advanced programming function lets you identify and extract all of the subexpressions in the simplified result of expression1.
For example, if expression1 simplifies to cos(π* x+3):
• The cos() function has one argument: (π* x+3).
• The sum of (π* x+3) has two operands: π* x and 3.
• The number 3 has no arguments or operands.
• The product π* x has two operands: p and x.
• The variable x and the symbolic constant p have no arguments or operands.
If x has a numeric value and you press diamond enter, the numeric value of π* x is calculated, the result is added to 3, and then the cosine is calculated.
cos() is the top-level operator because it is applied last.
part(expression1) ⇒ number
Simplifies expression1 and returns the number of top-level arguments or operands. This returns 0 if expression1 is a number, variable, or symbolic constant such as π, e, i, or ∞.
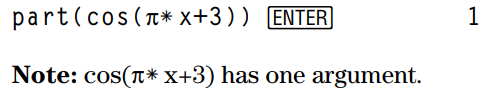
part(expression1, 0) ⇒ string
Simplifies expression1 and returns a string that contains the top-level function name or operator. This returns string(expression1) if expression1 is a number, variable, or symbolic constant such as π, e, i, or ∞.
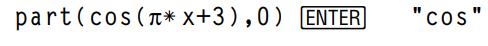
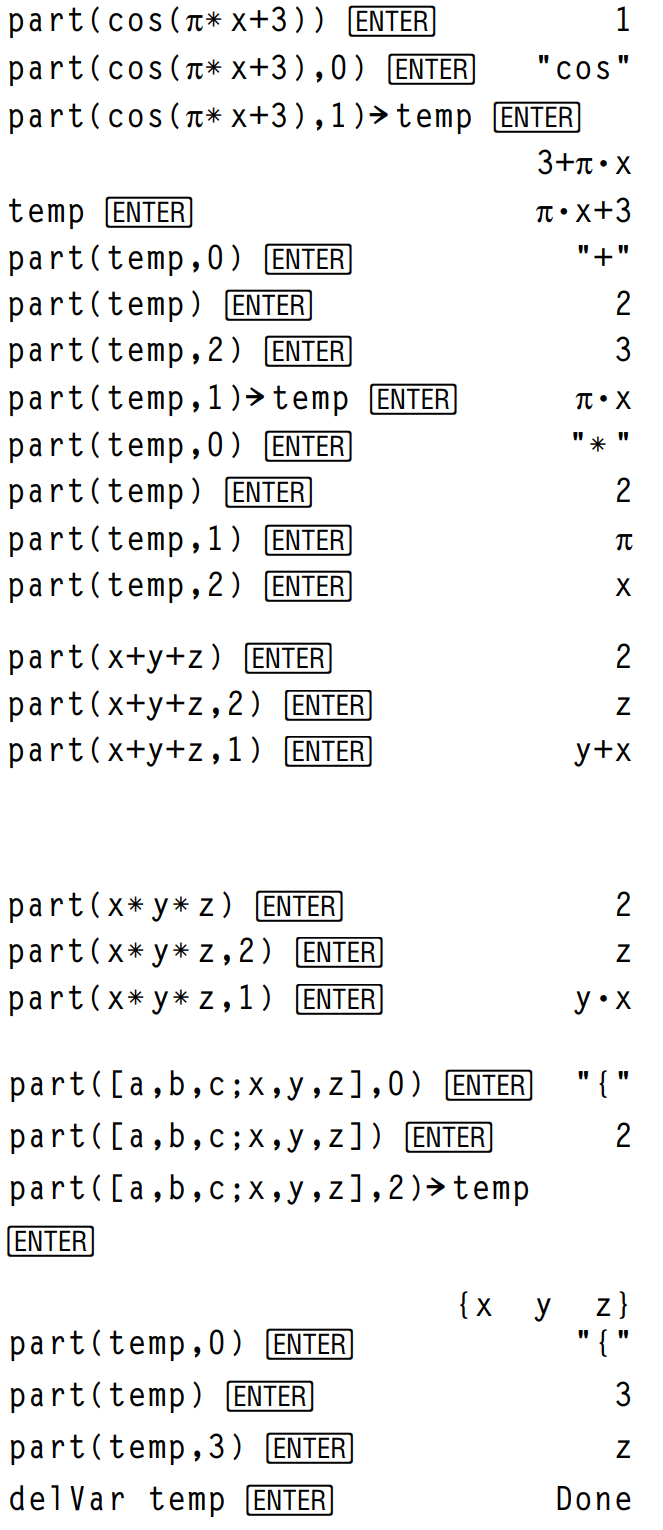
part(expression1, n) ⇒ expression
Simplifies expression1 and returns the nth argument or operand, where n is > 0 and ≤ the number of top-level arguments or operands returned by part(expression1). Otherwise, an error is returned.

By combining the variations of part(), you can extract all of the sub-expressions in the simplified result of expression1. As shown in the example to the right, you can store an argument or operand and then use part() to extract further sub-expressions.
Note: When using part(), do not rely on any particular order in sums and products.
Expressions such as (x+y+z) and (x-y-z) are represented internally as (x+y)+z and (x-y)-z. This affects the values returned for the first and second argument. There are technical reasons why part(x+y+z,1) returns y+x instead of x+y.
Similarly, x*y*z is represented internally as (x*y)*z. Again, there are technical reasons why the first argument is returned as y•x instead of x•y.
When you extract sub-expressions from a matrix, remember that matrices are stored as lists of lists, as illustrated in the example to the right.
The example Program Editor function to the right uses getType() and part() to partially implement symbolic differentiation. Studying and completing this function can help teach you how to differentiate manually. You could even include functions that the TI-89 / TI-92 Plus cannot differentiate, such as Bessel functions.

- 1

세상의모든계산기 님의 최근 댓글
오류 발생 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dcg0x5SjETY 위 영상의 문제의 함수를 직접 구해 보았습니다. 그래프로는 잘 확인이 되는데... fmin(), fmax() 함수로 직접 구해보니, 결과가 기대한 것과 다르네요. 구간을 넣지 않으니 fmim, fmax 둘 다에서 오류인 결과를 내놓습니다. 구간을 넣더라도, 적절하게 넣지 않으면, 답이 잘 안나오는 걸 확인할 수 있습니다. fmin 은 그나마 x=0을 기준으로 나누지 않더라도 답이 나오는 편이지만, fmax 는 -10~10 을 구간으로 넣을 때, 가운데 x=0 근방에서 그래프가 위로 솟아오르는 구간은 함수값을 확인하지 않는 듯 합니다. ㄴ fmax가 더 열등해서 그런 것은 아니고, 뒤집어진 모양에서는 반대로 fmin이 못찾습니다. 구간 범위가 커질 경우, 함수에 적용하여 계산하다가 숫자 허용 한계를 벗어나서 overflow 가 나서 오류가 발생할 수도 있는 듯 합니다. 뒤에 점을 넣으니 경고 문구가 추가로 나오긴 했는데, ⚠️ Questionable accuracy. When applicable, try using graphical methods to verify the results. 그래도 실망이네요. * 믿음직한 녀석은 아닌 듯 하니, 주의 표시 ⚠️가 나오든 안나오든, 사용에 주의하시기 바랍니다. 가급적이면 그래프로 검증해 보시는게 좋겠습니다. 2025 10.26 예시 8-1 : 분수식 solve시 오류 예시, 분모에 들어간 X³을 X로 치환해 해결? https://allcalc.org/56074 2025 10.25 fx-570 CW 는 아래 링크에서 https://allcalc.org/56026 2025 10.24 불러오기 할 때 변수값을 먼저 확인하고 싶을 때는 VARIABLE 버튼 【⇄[x]】목록에서 확인하고 Recall 하시면 되고, 변수값을 이미 알고 있을 때는 바로 【⬆️SHIFT】【4】로 (A)를 바로 입력할 수 있습니다. 2025 10.24 fx-570 CW 로 계산하면? - 최종 확인된 결과 값 = 73.049507058478629343538 (23-digits) - 오차 = 6.632809104889414877 × 10^-19 꽤 정밀하게 나온건 맞는데, 시뮬레이션상의 22-digits 와 오차 수준이 비슷함. 왜 그런지는 모르겠음. - 계산기중 정밀도가 높은 편인 HP Prime CAS모드와 비교해도 월등한 정밀도 값을 가짐. 2025 10.24