- TI nspire
[TI-nspire] (프로그램) 보간법 (선형, 다항식) Linear & Polynomial Interpolation
Linear & Polynomial Interpolation for TI-Nspire
Ver 1.2
by allcalc.org
-----
Usage
1. Input each x1,y1,x2,y2... var_x and var_y alternately
or matrix (2*n) type DATA at prompt for DATA.x
2. When you finished to insert DATA, type "end" at prompt for DATA.x
3. If there's no error with DATA sets, function i.linear() and i.polynomial() will be created.
4. Use functions to find unkown value "y"
5. Additionally, data.sub(matrix) and data.subx,data.suby(list) will be made too.
Caution
To stop a program that contains a Request command inside an infinite loop:
• Handheld: Hold down the "on" key and press "enter" repeatedly.
• Windows?: Hold down the "F12" key and press "Enter" repeatedly.
• Macintosh?: Hold down the "F5" key and press "Enter" repeatedly.
1. 기능
기본 데이터를 입력하여 선형 보간법에 따른 조각함수(Piecewise Function) i.linear(x) 와 다항식 보간법(라그랑주)에 따른 함수 i.polynomial(x) 를 생성합니다.
생성된 함수를 이용하여 특정 값(x)에서의, 보간법 예상치(y)를 구합니다.
2. 사용법
2-a. 기본 데이터 입력
- 프로그램의 실행 : inter()
- 기본 DATA 입력
방법 1 : 번갈아 입력 : x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3... , (입력이 끝나면 e 또는 end 를 입력)
혹은
방법 2 : 2×N 행렬을 한꺼번에 입력 : x값 입력시에 입력 - DATA 입력시
 주의사항
주의사항
* x 는 크기 순서로 입력할 필요 없음 (자동 sort 됨)
* (x,y) 데이터 쌍이 중복 되어도 괜찮으나, 하나의 x값에 둘 이상의 y값이 존재하면 에러 발생
2-b. 결과 함수의 이용
- 2-a의 입력이 끝나면 결과함수로 사용할 변수명을 물어봄
- 결과함수를 이용하여 추정값을 구함
ex) i.linear(3) 【Enter】 : x=3일 때의 추정값을 구함
2-c. 생성된 함수의 확인 http://www.allcalc.org/5752
- 【MENU】 【1】 【2】 (Action - Recall Definition) 명령으로 사용자 함수에 현재 정의되어 있는 내용을 확인할 수 있습니다.
3. 결과

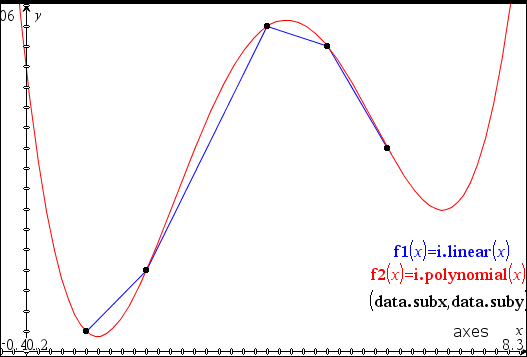
4. 소스코드
Define LibPub inter()=
Prgm
:© Linear and Polynomial Interpolation for TI-nspire
:© Ver 1.2
:© by allcalc (allcalc.org)
:
:© Part A: Input DATA
:
:Local n,data.x,data.y,data
:n:=0
:Loop
: Request "data.x or matrix(2×n) or END",data.x,0
:
:© Exit Loop Condition
: If string(data.x)="end" or string(data.x)="END" or string(data.x)="e" Then
: Exit
: EndIf
:
:© Adding Data
: n+1→n
:© Adding Data with Matrix
: If getType(data.x)="MAT" Then
: n+dim(data.x)[2]-1→n
: If n=dim(data.x)[2] Then
: data.x→data
: Else
: augment(data,data.x)→data
: EndIf
:© Adding Each Data Pair
: Else
: Request "data.y for x="&string(data.x),data.y,0
: If string(data.y)="end" or string(data.y)="END" Then
: Exit
: EndIf
: If n=1 Then
:[[data.x][data.y]]→data
: Else
: augment(data,[[data.x][data.y]])→data
: EndIf
: EndIf
:EndLoop
:
:© Part B : Data Processing
:
:© Part B1 : Data Processing
:Local data.listx,data.listy
:mat▶list(data[1])→data.listx
:mat▶list(data[2])→data.listy
:SortA data.listx,data.listy
:colAugment(list▶mat(data.listx),list▶mat(data.listy))→data
:
:© Part B2 : Section Verification&Consolidation and Slope
:© Verification
:Local i,j,dup
:newList(n)→dup
:For i,1,n-1
: If data[1,i]=data[1,i+1] Then
: 1→dup[i+1]
: If data[2,i]≠data[2,i+1] Then
: Disp "Data Error : ",[["x"]["y"]],"=",subMat(data,1,i,2,i+1)
: Stop
: EndIf
: EndIf
:EndFor
:
:© Consolidation
:© Local data.sub : Make data.sub global var
:subMat(data,1,1,2,1)→data.sub
:For i,2,n
: If dup[i]=0 Then
: augment(data.sub,subMat(data,1,i,2,i))→data.sub
: EndIf
:EndFor
:
:mat▶list(data.sub[1])→data.subx
:mat▶list(data.sub[2])→data.suby
:Disp "data.sub",[["x"]["y"]],"=",data.sub
:
:© Slope for Linear Interpolation
:Local sub.slope,sub.n
:dim(data.sub)[2]→sub.n
:newList(sub.n-1)→sub.slope
:For i,1,sub.n-1
:((data.sub[2,i+1]-data.sub[2,i])/(data.sub[1,i+1]-data.sub[1,i]))→sub.slope[i]
:EndFor
:
:
:© Part C1 : Out Polynomial Function as i.polynomial(x)
:Local poly,f_name
:"i"→f_name
:Request "Input Function name",f_name,0
:If getType(f_name)="NUM" Then
:"i"&string(f_name)→f_name
:Else
: If getType(f_name)≠"STR" Then
: string(f_name)→f_name
: EndIf
:EndIf
:
:"Define "&f_name&".polynomial(var_x)="&string(∑(data.sub[2,i]*∏(when(i≠j,((var_x-data.sub[1,j])/(data.sub[1,i]-data.sub[1,j])),1),j,1,sub.n),i,1,sub.n))→poly
:expr(poly)
:
:© Part C2 : Out Piecewise Linear Interpolation Function as i.linear(x)
:
:Local pf,random.x
:"Define "&f_name&".linear(x)=piecewise("→pf
:For i,1,sub.n-1
: pf&string(sub.slope[i]*(x-data.sub[1,i])+data.sub[2,i])&","&string(data.sub[1,i]≤x≤data.sub[1,i+1])&","→pf
:EndFor
:left(pf,dim(pf)-1)&")"→pf
:expr(pf)
:
:© Part C3 : Display functions usage
:rand()*(data.sub[1,sub.n]-data.sub[1,1])+data.sub[1,1]→random.x
:Disp "Usage : "&f_name&".linear("&string(random.x)&")=",#(f_name&".linear")(random.x)
:Disp f_name&".polynomial("&string(random.x)&")=",#(f_name&".polynomial")(random.x)
:
:Disp "Linear function is =",pf
:Disp "Polynomial function is =",poly
:EndPrgm
댓글10
-
세상의모든계산기
이 프로그램은 선형 보간법과 라그랑주 보간법을 동시에 구하는 프로그램입니다.
간단하게 선형 보간법의 결과만 필요한 경우에는
별도의 프로그램 파일 혹은 라이브러리를 사용하기보다 statistics(통계) 의 Linear Regression 기능을 이용하는 것이 편합니다.(예제 : http://www.allcalc.org/7826 )
- 1
-
세상의모든계산기
예를 들어
http://www.allcalc.org/2387 의 댓글에 있는 예제를 푼다면
【inter()】
【200】【1250】
【300】【1890】
【e】【Enter】
순으로 DATA 입력을 마치고【i.linear(250)】
으로 목표값을 찾습니다.* 이렇게 DATA 가 2쌍 뿐인 경우에는 i.linear() 함수와 i.polynomial() 함수가 동일한 결과값을 출력합니다.
(단, linear() 함수는 조각함수라서 데이터 범위 안쪽의 값만을 구할 수 있습니다.) - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
3
세상의모든계산기
inter() 함수 결과에 생성된 함수를 출력하는 명령(Disp)을 추가했습니다.
한 줄 표기되어서 알아보기 어렵다고 느끼실 때는
- Menu - Action - Recall Definition
- 아니면 한 줄 표기된 결과를 선택해서 입력창에 붙여넣기 하신 다음 [enter] 하시면 입체적 표현으로 바뀝니다.


세상의모든계산기 님의 최근 댓글
[fx-570 ES] 과학 상수를 이용한 계산에서 에러 발생 상황 https://kin.naver.com/qna/detail.naver?d1id=11&dirId=1118&docId=492235162&page=1&answerNo=1 vs 2026 03.01 과학상수를 이용한 계산 중 자릿수 한계로 인한 에러 발생 가능성 https://allcalc.org:443/board_calculators/6925#comment_57029 2026 03.01 기본 어댑터 MODEL : AD0301-1202500GB INPUT : 100~240V, 50~60Hz, 0.8A Max OUTPUT : 12.0V, 2.5A, 30.0W ㄴ 측정시 플러그 외경/내경 : 5.5mm / 2mm 2026 02.15 엑셀 파일로 만드니 전체 160~200MB 정도 나옵니다. 읽고 / 저장하는데 한참 걸리네요. 컴 사양을 좀 탈 것 같습니다. -> 엑셀/한셀에서 읽히지만, 구글 스프레드시트에서는 열리지 않네요. 100만 개 단위로 끊어서 20MB 정도로 분할해 저장하는 편이 오히려 속 편할 것 같습니다. -> 이건 구글 스프레드시트에서도 열리긴 하네요. (약간 버퍼링?이 있습니다) 2026 02.10 엑셀 / 행의 최대 개수, 열의 최대 개수, 셀의 최대 개수 엑셀의 행 개수 제한은 파일 형식에 따라 다르며, 최신 .xlsx 파일 형식은 시트당 최대 1,048,576행까지 지원하지만, 구형 .xls 파일은 65,536행으로 제한됩니다. 따라서 대용량 데이터를 다룰 때는 반드시 최신 파일 형식(.)으로 저장해야 하며, 행과 열의 총 수는 1,048,576행 x 16,384열이 최대입니다. 주요 행 개수 제한 사항: 최신 파일 형식 (.xlsx, .xlsm, .xlsb 등): 시트당 1,048,576행 (2^20). 구형 파일 형식 (.xls): 시트당 65,536행 (2^16). 그 외 알아두면 좋은 점: 최대 행 수: 1,048,576행 (100만여개) 최대 열 수: 16,384열 (XFD) 대용량 데이터 처리: 65,536행을 초과하는 데이터를 다루려면 반드시 .xlsx 형식으로 저장하고 사용해야 합니다. 문제 해결: 데이터가 많아 엑셀이 멈추거나 오류가 발생하면, 불필요한 빈 행을 정리하거나 Inquire 추가 기능을 활용하여 파일을 최적화할 수 있습니다. 2026 02.10