- TI nspire
[TI-nspire] 계산기 초기화 Reset, Document / Problem / Page / Variables 도큐먼트에서 변수까지
1. TI-nspire 의 특징
TI-nspire 는 간단하게 계산할 수 있는 Scratchpad  모드가 있고, 정식?으로 계산할 수 있는 Document
모드가 있고, 정식?으로 계산할 수 있는 Document  모드가 있습니다.
모드가 있습니다.
설명: Document, Problem, Page의 관계
문서(Document)
- 정의: Document(문서)는 하나의 File(파일)로 볼 수 있습니다.
- 특징: 하나의 문서에는 여러 개의 문제(Problem)를 포함할 수 있습니다.
문제(Problem)
- 정의: 문제는 문서 안에 생성되는 개별 단위입니다.
- 특징: 각 문제는 독립적이며, 다른 문제와 변수나 계산 결과를 공유하지 않습니다.
- 하위 단위: 각 문제는 여러 개의 페이지(Page)를 포함할 수 있습니다.
페이지(Page)
- 정의: 페이지는 문제 안에 생성되는 하위 단위입니다.
- 특징: 같은 문제 안의 페이지들은 서로 변수를 공유합니다.
- 제한: 계산 결과(ans)는 페이지들 간에 공유되지 않습니다.
Document (File)
├── Problem 1
│ ├── Page 1
│ ├── Page 2
│ └── Page 3
├── Problem 2
│ ├── Page 1
│ ├── Page 2
│ └── Page 3
└── Problem 3
├── Page 1
├── Page 2
└── Page 3
관계 요약
- Document는 여러 Problem을 포함.
- 각 Problem은 서로 독립적이며, 변수나 계산 결과를 공유하지 않음.
- Problem 내부의 Page는 변수를 공유하지만, 계산 결과(ans)는 공유하지 않음.
여러 단계로 구분된만큼 DATA를 초기화하는 단계도 다양합니다. 원하는 수준으로 초기화하고 새로운 계산을 하는 것은 DATA를 관리하는데 중요한 일입니다.
예를 들어
현재 계산과정은 보존한 채 변수를 공유하는 다른 작업을 하고 싶으면 새 Page를 만들고,변수가 섞이면 안되는 다른 작업을 하고 싶으면 새 Problem 이나 새 Document 를 만들면 됩니다.
ㄴ 작업간 유사성이 있다면 New Problem 으로 하나의 파일에 저장시켜두는 것이 유리하겠죠.
2. 초기화
1. 계산기 전체 초기화
* 효과
: 메모리에 저장되어 있는 (Mylib 폴더를 포함한) 모든 file들을 삭제하고 공장 초기화 상태에 가깝게 돌립니다.
* 방법 :
 = My Document 파일 관리자 화면
= My Document 파일 관리자 화면 

 = DELETE All
= DELETE All 
 = OK 재확인
= OK 재확인
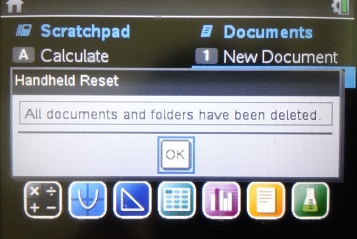
※ 시험을 위한 초기화에 적합합니다. 되돌리기 명령 
 이 통하지 않습니다.
이 통하지 않습니다.
시험 감독관이 위의 명령을 직접 시행하는 것이 가장 좋고, 아니면 최소한 아래의 화면을 확인하여야 합니다.
2. Document 삭제 & 새 Document 생성
* 새 Document 생성 : 

ㄴ 이 때 기존 작업중이던 Document 를 저장할 것인지 묻는데, No 를 선택하면 자동으로 삭제되는 효과를 얻습니다.
* 기존 Document 삭제 : 

 해당 파일 선택 후
해당 파일 선택 후 

 주의
주의
다만 삭제 직후에 
 = 되돌리기 기능을 사용하면 파일삭제 명령을 되돌릴 수 있습니다.
= 되돌리기 기능을 사용하면 파일삭제 명령을 되돌릴 수 있습니다.
따라서 완벽한 초기화를 하려면 'My Document' 만 보고 판단하지 말고, 『1. 계산기 전체 초기화』 명령을 반드시 확인하여야 합니다.
3. 현재 Problem 삭제 or 새 Problem 생성
* 새 Problem 생성 : 
 = Insert
= Insert 
 = Problem
= Problem
* 현재 Problem 삭제 : 
 = Page Sorter 로 이동
= Page Sorter 로 이동
 방향키로 삭제할 Problem 을 (검정색) 하이라이트시키고
방향키로 삭제할 Problem 을 (검정색) 하이라이트시키고 
4. 현재 Page 삭제 or 새 Page 생성
* 새 Page 생성 : 
 또는
또는 

ㄴ 둘 다 같은 효과
* 현재 Page 삭제 : 
 = Page Sorter 로 이동
= Page Sorter 로 이동
 방향키로 삭제할 Page에 (테두리) 하이라이트시키고
방향키로 삭제할 Page에 (테두리) 하이라이트시키고 
ㄴ 선택한 Page가 속한 Problem 의 모든 Page가 삭제되면 Problem 도 같이 삭제됨
스크래치 패드 에서는
에서는 
 Clear Scratchpad 가 같은 기능을 합니다.
Clear Scratchpad 가 같은 기능을 합니다.
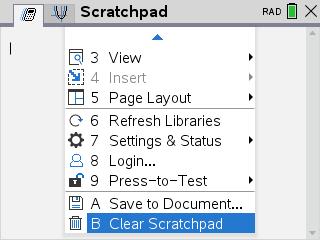
5. 변수만 삭제
* ClearAZ : 



ㄴ a에서 z까지 영문자 1글자로만 이루어진 변수(함수)만 삭제.
ㄴ 삭제되지 않는 변수(함수)명 예시 : a1, ab, f1()
* delvar 변수명(들) : 


ㄴ 변수들은 컴마(,)로 구분하여 입력
6. 현재 Page 내 모든 entry 청소
모든 작업 과정 제거 : 

 = Clear History
= Clear History
ㄴ 작업의 결과로서 변수에 저장된 내용 등이 삭제되는 것은 아님
댓글11
- 1
- 1
- 1
-
1
세상의모든계산기
1-1. 최초 mylib 폴더 안에는 linalgcas.tns 와 numtheory.tns 라이브러리가 들어 있습니다. (이 댓글에 첨부합니다)
linalgcas library
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Part1: Linear Algebra
ceigenvals(Matrix)- symbolic complex eigenvalues of a matrix
clearmat()- delete temporary matrices
cofactor(Matrix,i,j) - cofactor of a matrix
comatrix(Matrix) - comatrix of a matrix (matrix of cofactors)
diagonalization(Matrix)- matrix diagonalization
dn(Matrix)- Jordan–Chevalley decomposition of a matrix M, where M=D+N, N·D=D·N
eigenvals(Matrix)- symbolic real eigenvalues of a matrix
eigenvects(Matrix,λ)- symbolic basis of the eigenspace of a matrix related to eigenvalue λ.
expmat(Matrix)- symbolic matrix exponential, ^(t·Matrix).
gausstep(Matrix)- step-by-step row matrix reduction.
help()- displays syntax info for functions and programs from library linalgcas.
inversestep(Matrix)- step-by-step matrix inverse computation.
kernelbasis(Matrix)- basis of kernel (null space) of a square matrix
kernelvectors(Matrix)- kernel (null space) vectors of a matrix
pwrmat(Matrix)- symbolic matrix power,Matrix^(n)
rank(Matrix)- rank of a matrix
simultstep(aMatrix, bVector)- step-by-step version of simult().
Part2: System of Linear Differential Equations
desystem(A,B)- solve system of differential equations in the form X'(t)=A·X(t)+B(t)
desysinitcond(A,B,t0,X0)- solve above system with initial condition X(t0)=x0.
desysnewcond(t1,X1)- solve the previously solved system of linear differential equations again, but with new initial conditions X(t1)=X1
numtheory library (en/fr/ge) - version 1.00 (2009-02-17)
Public functions for arithmetic
bezout(a,b) - (u,v,d)such that ua+bv=d, with d=gcd(a,b)
contfrac2real(list)- converts the continued fraction list to a real number
divisors(n)- list of divisors of n
factorstep(n)- step-by-step factorization of integer n
gcdstep(a,b)- step-by-step gcd
listprimediv(n)- list of prime divisors
nextprime(n)- first prime psuch that n≤p
phi(n)- number of positive integers not exceeding n and relatively prime to n
prevprime(n)- last prime psuch that p≤n
primecount(a,b)- counts the primes between aand b
primelist(a, b)- generates the list of primes between aand b
pwrmod(a,n,b)- compute a^(n) mod b(even for large values of aand n)
real2contfrac(num,k)- generates a list of the first k convergents for the continued fraction of a real number num.
Public functions for study of permutations
randperm(n)- generate a random permutation of {1,2,3,...,n}
signature(σ)- signature of a permutation defined by the list {σ(1),σ(2),...}
signaturestep(σ)- step-by-step signature of a permutation, with intermediate steps (with display of the decomposition in disjoint cycles)
Others tools included in this library
select(List,"boolean_expr(x)")- selects elements of a list with a specified property
select_range(n1,n2,"boolean_expr(x)")- selects integers elements between n1and n2with a specified property
sort_asc(ListNum)- sorts a list of numeric values in ascending order
sort_desc(ListNum)- sorts a list of numeric values in descending order
Private functions
These functions are not shown in the catalog, but they may however be used in other documents, if they are called by their long names.
numtheory\is_perm(List)- tests if a list does define a permutation: elements must be integers from 1 to n (number of elements of the list) and each must appear exactly once.
- 2
- 3

세상의모든계산기 님의 최근 댓글
2번 사진 3개 사진 공통적으로 구석(corner) 에 증상이 있다는 특징이 있네요. 영상 찾아보니 이 가능성이 가장 높은 듯 합니다. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zxRBohepzwc ㄴ Liquid Crystal Leakage (액정 누설). ㄴ 손으로 밀어내니 주변으로 밀려나네요. 그래서 점으로 보이기도 하구요. 2025 10.29 500! 의 십진수 근사값 확인 500! = 1.22013682599111006870123878542304692625357434280319284219241358838 × 10^(1134) (참값, 울프람 알파) 2025 10.29 관련 라이브러리 https://allcalc.org/56263 sgn(x) 내장된 부호 함수(signum function)와 달리, 이 함수의 sgn(0)은 0을 반환합니다. 2025 10.29 라이브러리로 사용할 수 있습니다. (제작자 추천) 1. mylib 폴더에 넣기 2. Actions ➡️ library ➡️ refresh libraries 실행 하기 2025 10.29 ChatGPT-5 기호(÷, /, :) 자체는 의미적으로 같은 “나눗셈”을 뜻하지만, 문맥(사람이 쓰는 수학 vs 컴퓨터/프로그래밍)에 따라 해석 우선순위가 달라질 수 있습니다. 🔹 1️⃣ 전통 수학 표기 — ÷, /, : 수학 교과서, 논문, 일반 문서 등에서는 셋 다 의미적으로 “나누기”로 간주됩니다. 즉, 48÷2(9+3), 48/2(9+3), 48:2(9+3) 은 같은 의미로 받아들여야 합니다. 모두 사람의 수학 관행적 해석이 적용되어 48 ÷ 2 × (9+3) = 288 로 처리되죠. 즉, 기호가 바뀌어도 결과는 바뀌지 않습니다. 🔹 2️⃣ 컴퓨터·프로그래밍 문맥에서 / 사용 시 컴퓨터는 “생략된 곱셈(implicit multiplication)”을 따로 구분하지 못합니다. 따라서 다음 두 식은 완전히 다르게 인식됩니다. 표현 파이썬 등에서 해석 결과 48 / 2*(9+3) ((48 / 2) * (9+3)) 288 48 / 2(9+3) ❌ 문법 오류 (생략된 곱셈 인식 불가) — 즉, 컴퓨터 언어에서는 생략된 곱셈이 허용되지 않기 때문에, /는 반드시 명시적 *와 함께 써야 합니다. 🔹 3️⃣ “:” 기호의 경우 현대 수학에서는 “비율”을 나타내는 기호로 쓰입니다. a:b = \frac{a}{b} 따라서 (27 : 3(1+2)3) 같은 표현은 모호하거나 비표준적으로 간주됩니다. 대부분의 경우 계산기로는 입력 자체가 불가능합니다. ✅ 정리 기호 의미 결과 변화 주로 쓰이는 문맥 ÷ 나누기 없음 초중등 수학, 일반 표기 / 나누기 없음 (단, 프로그래밍에서는 생략 곱 불허) 수학/컴퓨터 : 비율 (또는 나누기 의미로 혼용) 보통 계산식에서는 사용 안 함 비, 비율 표기 🔹 결론 48 ÷ 2(9+3), 48/2(9+3), 48:2(9+3) 는 “수학적 의미”로는 동일하게 81로 해석됩니다. 하지만 프로그래밍이나 수식 파서(context) 에서는 /만 유효하고, 생략된 곱은 허용되지 않으며, :는 아예 다른 의미(비율)로 인식됩니다. 2025 10.28