- TI nspire
[TI-nspire CAS] function - desolve() : 미분방정식 함수
1. 개요
미분방정식의 해를 구하는 함수입니다.
※ TI-89T의 desolve() 함수와 비슷한 기능을 합니다. ( 똑같지는 않은 듯)
2. 사용방법
2-1. 일반해
deSolve(1stOr2ndOrderODE, Var, depVar) ⇒ a general solution
Returns an equation that explicitly or implicitly specifies a general solution to the 1st- or 2nd-order ordinary differential equation (ODE). In the ODE:
- Use a prime symbol (press 【?!▶】) to denote the 1st derivative of the dependent variable with respect to the independent variable.
- Use two prime symbols to denote the corresponding second derivative.
The prime symbol is used for derivatives within deSolve() only. In other cases, use d().
The general solution of a 1st-order equation contains an arbitrary constant of the form ck, where k is an integer suffix from 1 through 255. The solution of a 2nd-order equation contains two such constants. Apply solve() to an implicit solution if you want to try to convert it to one or more equivalent explicit solutions.
When comparing your results with textbook or manual solutions, be aware that different methods introduce arbitrary constants at different points in the calculation, which may produce different general solutions.
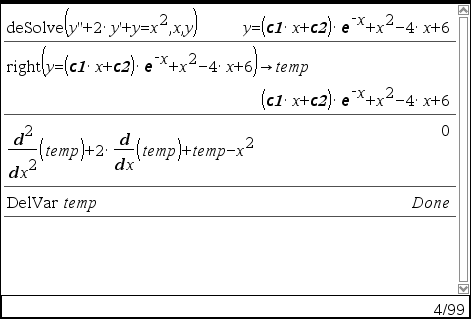
2-2. 특수해
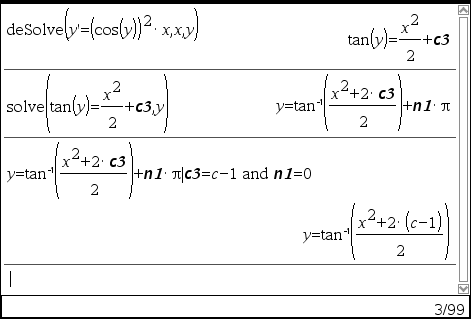
deSolve(1stOrderODE and initCond, Var, depVar) ⇒ a particular solution
Returns a particular solution that satisfies 1stOrderODE and initCond. This is usually easier than determining a general solution, substituting initial values, solving for the arbitrary constant, and then substituting that value into the general solution.
initCond is an equation of the form:
depVar (initialIndependentValue) = initialDependentValue
The initialIndependentValue and initialDependentValue can be variables such as x0 and y0 that have no stored values. Implicit differentiation can help verify implicit solutions.

2-3. 특수해
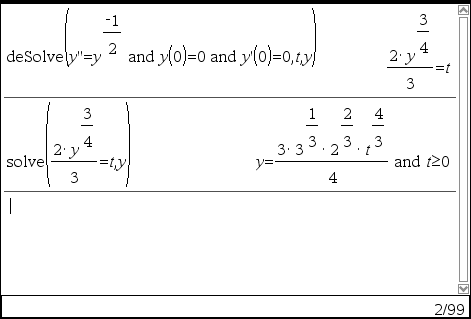
deSolve(2ndOrderODE and initCond1 and initCond2, Var, depVar) ⇒ particular solution
Returns a particular solution that satisfies 2nd Order ODE and has a specified value of the dependent variable and its first derivative at one point.
For initCond1, use the form:
depVar (initialIndependentValue) = initialDependentValue
For initCond2, use the form:
depVar (initialIndependentValue) = initial1stDerivativeValue
2-4. 특수해
deSolve(2ndOrderODE and bndCond1 and bndCond2, Var, depVar) ⇒ a particular solution
Returns a particular solution that satisfies 2ndOrderODE and has specified values at two different points.
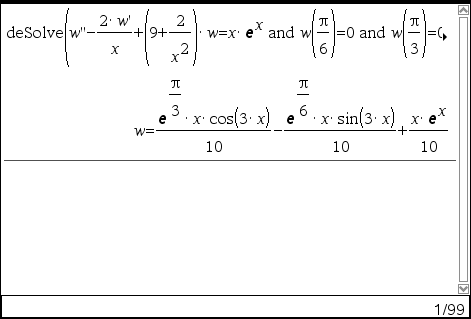
3. 주의사항
※ 내용 출처 : TI-Nspire™_ReferenceGuide_EN_V3.9.pdf
댓글15
-
세상의모든계산기
Q : 어떤 박테리아의 개체수가 증가하는 속도는 현재의 개체수에 비례하여 증가한다고 한다. 10일 후에 박테리아 개체수가 현재의 2배가 된다면, (현재로부터) 25일 후에는 현재의 몇배가 되나?
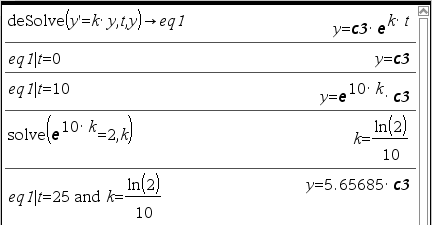
-
세상의모든계산기
Q1 : 박테리아 배양기에 200개의 개체가 있다고 하자. 60분 후에 650개의 개체가 관찰되었다. 지수적으로 증가한다고 하고 t분 후의 개체 수와 초기 개체 수로부터 개체 수가 2배가 될 때까지 걸린 시간을 구하자.
[출처] 수학-미분방정식의 모델 1|작성자 미분 연산자
ㄴ 원문은 "관찰되었다"가 아니고 "생성되었다"이지만, 혼동을 피하기 위해 변경하였습니다.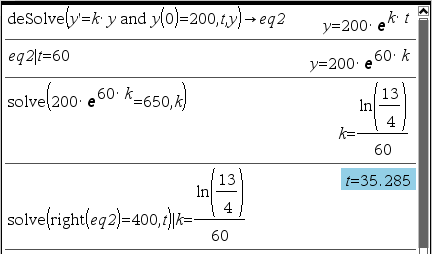
Q2 : 예를 들면 14C(탄소-14)의 반감기를 대략 5730년으로 계산하는데, 이 탄소를 1 gram 갖고 있다면 5730년 후에는 대략 0.5 gram 이 남아 있게 된다. 지금 14C를 100 gram 갖고 있다면 250년 후에는 얼마나 남을까?

ㄴ 방사성 동위원소를 이용한 실험 결과를 계산하는 과정을 설명하고 있습니다.위 반감기 남은 물질 방정식은 아래와 같이 바꿔 쓸 수도 있습니다. (지수-로그 공식)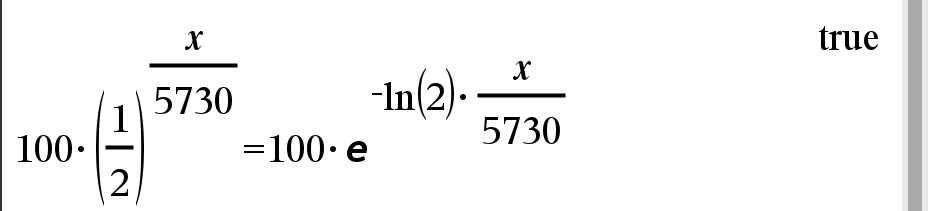
-
세상의모든계산기
Q3 : 선사시대의 벽화 연대를 측정하기 위하여 타버린 나무 조각이나 숯을 사용하였다. 타버린 나무 조각에서 C-14의 85.5%가 감소하였다면 이 나무의 연대를 결정하라?
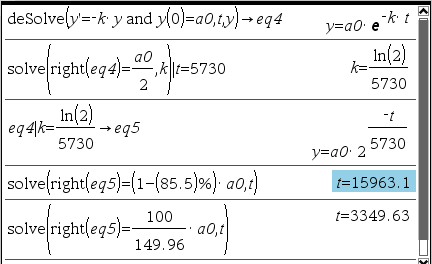
* 친절하게 몇%가 감소하였다고 나오지 않고, 붕괴율이 자료로 나온다면 그 아래 식으로 풀이
(시료의 붕괴율 R=100 min-1, 자연상태 붕괴율 R0=144.96 min-1) -
세상의모든계산기
문제
어떤 물질이 10시간에 6%씩 감소한다. 이 물질의 반감기를 찾아라.
Solution 1
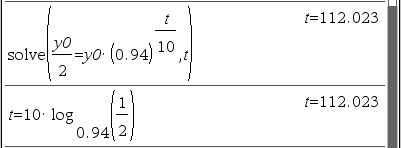
Solution 2
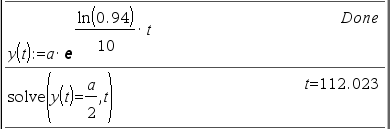
둘을 같은 풀이라고 할 수 있나? OK
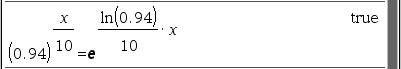
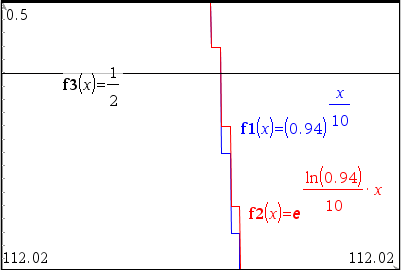
그래프 페이지에서 직접 확인해 보면 거의 일치하지만, 최대한으로 확대(zoom)해 보면 미~~세하게 차이가 남. (계산상 유효 자릿수 14 digts 한계 때문인 듯)
- 1
-
1
세상의모든계산기
잘 모르겠습니다. 그냥 우변을 0으로 놓으면 되는 것입니까?
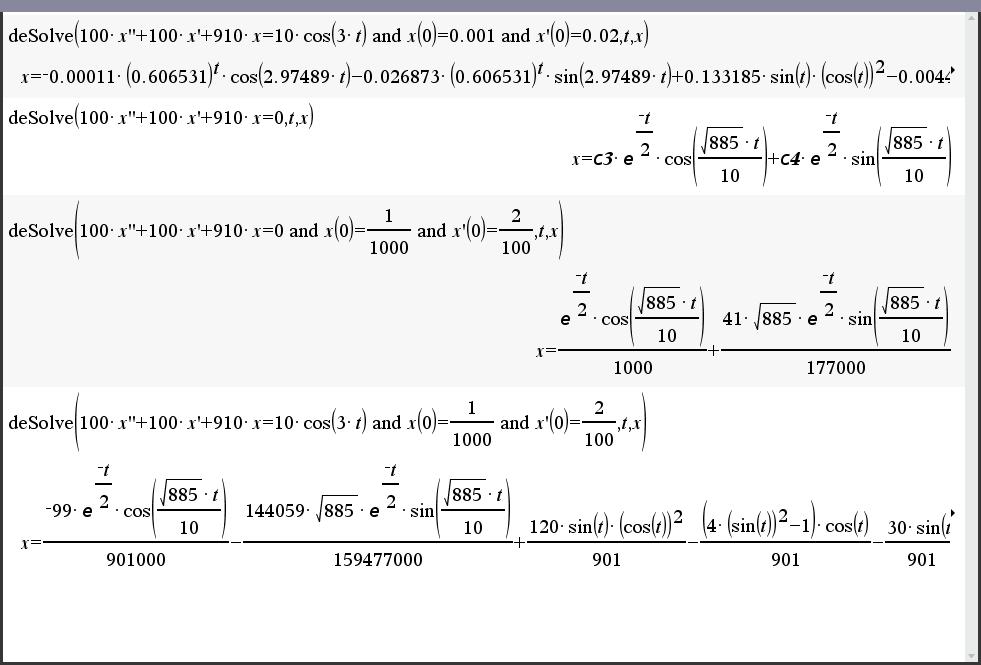
- 2
- 1
- 1

세상의모든계산기 님의 최근 댓글
은행앱 통합하면서 없어졌나보네요. ㄴ 비슷한 기능 찾으시는 분은 : 스마트 금융 계산기 검색해 보세요. https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.moneta.android.monetacalculator 2026 01.25 Ctrl+Z 를 이용해 뒤로 돌아기기 Undo 기능이 있는지 살펴보세요. 2026 01.23 쌀집계산기로 연립방정식 계산하기 - 크래머/크레이머/크라메르 공식 적용 https://allcalc.org/56739 3. 'x' 값 구하기 계산기 조작법 목표: x = Dx / D = [(c×e) - (b×f)] / [(a×e) - (b×d)] 계산하기 1단계: 분모 D 계산 (메모리 활용) 1 * 1 M+ : 메모리(M)에 1를 더합니다. (현재 M = 1) -0.1 * -0.2 M- : 메모리(M)에서 0.02를 뺍니다. (현재 M = 0.98 = 0.98) 이로써 메모리(MR)에는 분모 0.98가 저장됩니다. 2단계: 분자 Dx 계산 후 나누기 78000 * 1 : 78000를 계산합니다. = : GT에 더합니다. -0.1 * 200000 : -20000를 계산합니다. ± = : 부호를 뒤집어 GT에 넣습니다. // sign changer 버튼 사용 GT : GT를 불러옵니다. GT는 98000 (분자 Dx) 값입니다. ÷ MR = : 위 결과(98000)를 메모리(MR)에 저장된 분모 D(0.98)로 나누어 최종 x값 100,000를 구합니다. 4. 'y' 값 구하기 계산기 조작법 목표: y = Dy / D = [(a×f) - (c×d)] / [(a×e) - (b×d)] 계산하기 1단계: 분모 D 계산 (메모리 활용) 'x'에서와 분모는 동일하고 메모리(MR)에 0.98가 저장되어 있으므로 패스합니다. 2단계: 분자 Dy 계산 후 나누기 GT ± = : GT를 불러오고 부호를 뒤집어 GT에 더합니다. GT가 0으로 리셋됩니다. 【AC】를 누르면 M은 유지되고 GT만 리셋되는 계산기도 있으니 확인해 보세요. 1 * 200000 : 200000를 계산합니다. = : GT에 더합니다. 78000 * -0.2 : -15600를 계산합니다. ± = : 부호를 뒤집어 GT에 넣습니다. GT : GT를 불러옵니다. 215600 (분자 Dy) 값입니다. ÷ MR = : 위 결과(215600)를 메모리(MR)에 저장된 분모 D(0.98)로 나누어 최종 y값 220,000를 구합니다. x, y 값을 이용해 최종 결과를 구합니다. 2026 01.18 크레이머 = 크레머 = 크라메르 공식 = Cramer's Rule https://allcalc.org/8985 2026 01.18 부호 변경, Sign Changer 버튼 https://allcalc.org/52092 2026 01.18